Kettle Re – Using deep-learning to make climate-linked risks reinsurable
Kettle Re is launching as a reinsurance provider utilising deep-learning and artificial intelligence to create proprietary risk models and analytics that can help it more accurately and sustainably price climate-linked exposures, starting with wildfires.
 Every so often new start-ups come along that combine the best of the insurance technology (insurtech) wave, with first class underwriting and an ambition to make the resulting risk transfer as capital efficient as possible.
Every so often new start-ups come along that combine the best of the insurance technology (insurtech) wave, with first class underwriting and an ambition to make the resulting risk transfer as capital efficient as possible.
Enter Kettle, or Kettle Re, which announced this week that it has raised a $4.71 million seed financing round that was led by True Ventures, with participation from Acrew Capital, Anthemis, Homebrew Ventures, and Inspired Capital.
Kettle Re is a reinsurance provider that aims to leverage machine learning technology to better protect people from the growing risks associated with climate change, such as California’s wildfires.
Working with enormous data sets, Kettle Re uses its deep-learning systems to simplify, better understand and synthesize information on risk exposures and has put its technology to work at first on wildfires in California, a peril increasingly in focus and often cited as uninsurable in some quarters of the industry.
By having what it believes is a more accurate and sophisticated view of the risk, Kettle Re hopes to make the risk more understandable and therefore more appealing to reinsurance capital providers of all kinds, ultimately helping to make it more insurable.
Looking more broadly at the sphere of risks linked to climate change, Kettle Re has ambitions to expand beyond wildfire in time, but has chosen this peril to hone its tech.
Operating as a Bermuda based MGA, Kettle Re will leverage its proprietary software tools to make risks more understandable and to more accurately price and underwrite them, ultimately hoping to attract reinsurance capital to its programs and underwriting which it believes will be best-in-class as result of its technology advantage.
Kettle was founded by Andrew Engler, who has over a decade of insurance and reinsurance market experience most recently as VP of digital at Argo Group, and Nathaniel Manning, who has years of experience in data and disaster gained from humanitarian initiatives as the CEO of the largest open source software platform for community crisis response Ushahidi, and as the first chief data officer of USAID.
“Reinsurance is the last stop against climate change,” Engler said. “It’s the safety net below the safety net. As the frequency and severity of these events has increased in a dramatic non-linear fashion over the past 15 years, it’s imperative to bring the most advanced technology in the world to help combat its effects.”
“I’ve spent years building software to enable people to get help in the aftermath of a crisis,” Manning commented. “But I noticed it was the insurance companies who were providing the financial safety nets to help these communities rebuild. That’s why we founded Kettle, to make an impact.”
Also on-board at Kettle Re as Chairman and Chief Underwriting Officer (CUO) is Nigel Mortimer, most recently founder and President of Argo Group’s Bermuda insurance operations.
“Over the past decade there has been huge advances in the monitoring and modelling of human behaviour through social media. That’s great but actually now we need to urgently amp up the attention we pay to our host, planet earth. We have reached a threshold moment where we must make a choice, to continue to focus on ourselves or to try and understand better the earth’s changing behaviour and adapt ours accordingly. In San Francisco the world’s best data scientists literally have catastrophe on their doorstep and its driving a shift in priorities. At Kettle we are excited to be at the leading edge of that movement to refocus computer power to solve the biggest problem humanity has ever faced,” Mortimer explained.
Kettle’s first product is focused on wildfires and leveraging proprietary deep-learning technology called Swarm Neural Network intelligence, the firm’s model predicted 11 of the 14 major wildfires in the top 10% most likely zones to have a fire this year. Out of the top 20% most dangerous, Kettle predicted 14 of the 14.
Impressive results and this advanced catastrophe modelling technology and predictive analysis of climate perils puts to work impressive amounts of data as well.
9 billion lines of data from public and private data sources are utilised in a single run of the model, including sources like NOAA weather data and NASA’s MODIS and LIDAR satellites.
During a single model run, the swarm of 3,414 virtual machines runs an astounding 3 tredecillion calculations, 42.3 million simulations, and 140 million model parameters to calculate the probabilities of wildfire damage at the half square mile resolution across the state of California.
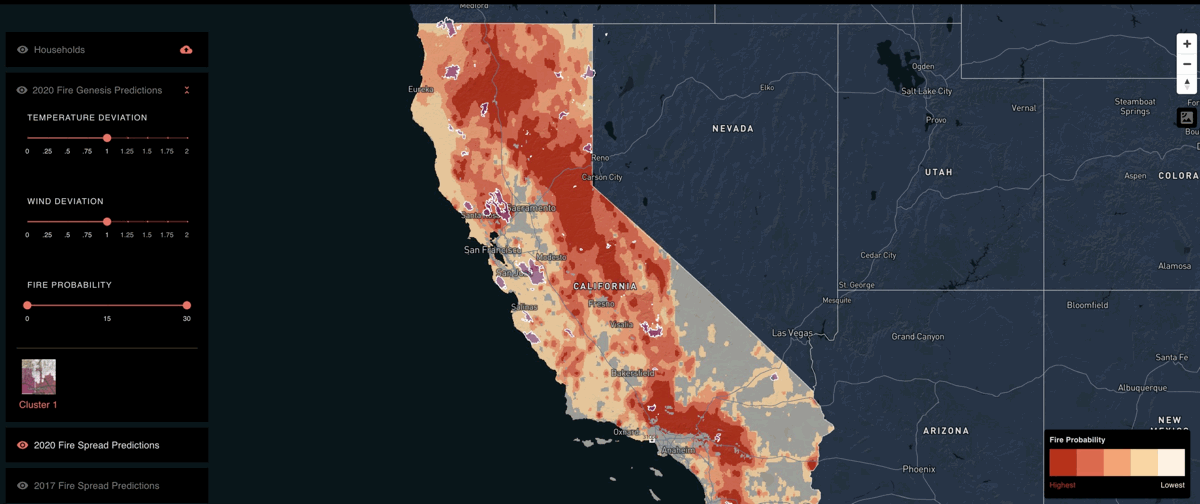
Step back for a moment to consider the ramifications of the use of such vast quantities of data to inform reinsurance risk analysis, pricing and underwriting and it quickly becomes clear that the industry is on the cusp of a new wave of understanding of the risks posed by specific perils, as well as the influence climate change is having on them.
It’s also clear that Kettle could take this kind of sophisticated tech and apply it to areas like flood risk, where inundation could have billions of possible end-scenarios within a single river flood basin, or in predicting the location of peak-wind damage from major storms. The list of use-cases is long and significant for the insurance and reinsurance industry.
As well as for the insurance-linked securities (ILS) market, of course.
Kettle Re has an ambition to be open and agnostic to capital forms and bringing capacity from the likes of ILS funds or investors into its underwriting programs as they scale is likely to be extremely desirable and a way to add greater cost-efficiencies into the system as well.
Kettle has every opportunity now to demonstrate the effectiveness of its models and create structures that enable different types of capital to access the risks it underwrites in an efficient manner.
Kettle believes it can bring significant innovation to reinsurance and ILS markets, because of the infinite scalability and high definition level of modeling capable on its platform.
“Along with higher accuracy in pricing risk from our current 84.7% F-1 score,” Kettle Co-founder and CTO Son le, who is also an Arog alum having been Head Quant of its Digital Division, said, “We have the ability to price risk on a home by home basis, potentially creating parametric products that trigger when a wildfire enters a grid or not.”
Kettle also believes its technology can help the industry provide shorter term covers, leveraging high-resolution pricing, meaning coverage could be given anywhere from 3, 6, or 9, month periods, to weeks or even days.
The company has also seen interest from multiple ILS funds in creating alternative structures to the traditional reinsurance market, where tranche based pricing related to actual burn probabilities and likelihood of fires affecting categories of homes could be used to provide different risk/return investment opportunities within the overall wildfire risk pool Kettle creates.
It’s a fascinating approach and if the modelling proves robust enough is certain to attract reinsurance and ILS capital support.
The ramifications for the industry are significant, as technology like Kettle, combined with its approach and desire to leverage efficient capacity, shows a way that reinsurance costs can be made more sustainable across portfolios of risk, ultimately helping to keep climate-linked risks more affordable and more importantly perhaps, better protected by insurance.
“We like to invest in companies that use technology to improve the world,” Adam D’Augelli, partner at True Ventures commented. “Reinsurance for climate-related events is an increasingly vital part of the insurance market and will continue to be. We’re thrilled to support mission-driven founders like Andrew (Engler), Nathaniel (Manning), Nigel (Mortimer) and Son (Le) who are using software to tackle big and important problems.”
We always talk about the insurability of climate risk and perils exposed to climate change. Perhaps this discussion should really be, how do we encourage and sustain the appetite of reinsurance capital to assume these exposures, to help the insurance industry do a better job of insuring against them.
One way is through advanced technology and risk analytics, enabling better pricing and more informed underwriting. The next way is through better and more responsive risk transfer structures and capital structures underpinning them.
As a result, Kettle Re and similar initiatives provide hope that technology can drive a better understanding of risk and use of capital at the reinsurance level, to the ultimate benefit of the insurance consumer.
Kettle Re – Using deep-learning to make climate-linked risks reinsurable was published by: www.Artemis.bm
Our catastrophe bond deal directory
Sign up for our free weekly email newsletter here.
Original Article Posted at : https://www.artemis.bm/news/kettle-re-using-deep-learning-to-make-climate-linked-risks-reinsurable/
